Navigating Growth: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Global Cargo Shipping Market
Exploring the Trends, Drivers, and Future Prospects Shaping the Global Cargo Shipping Industry
Introduction
The Cargo Shipping Market plays a vital role in global trade and the movement of goods, underpinning the world economy by facilitating the transportation of raw materials, intermediate goods, and finished products across continents. As one of the oldest and most cost-efficient means of transporting bulk goods, cargo shipping continues to evolve with technological advancements, shifting trade routes, and rising environmental concerns. The increasing demand for global trade, bolstered by the e-commerce boom and industrial growth, has made the cargo shipping market a focal point of strategic development for logistics companies and governments alike.
This article delves deep into the dynamics of the global cargo shipping market, exploring key trends, growth drivers, challenges, segmentation, regional insights, and future outlook.
Market Overview
The global cargo shipping market is a vast and dynamic sector, encompassing different types of vessels including container ships, bulk carriers, tankers, and roll-on/roll-off (Ro-Ro) vessels. The industry is heavily influenced by global economic trends, port infrastructure development, geopolitical shifts, and trade regulations.
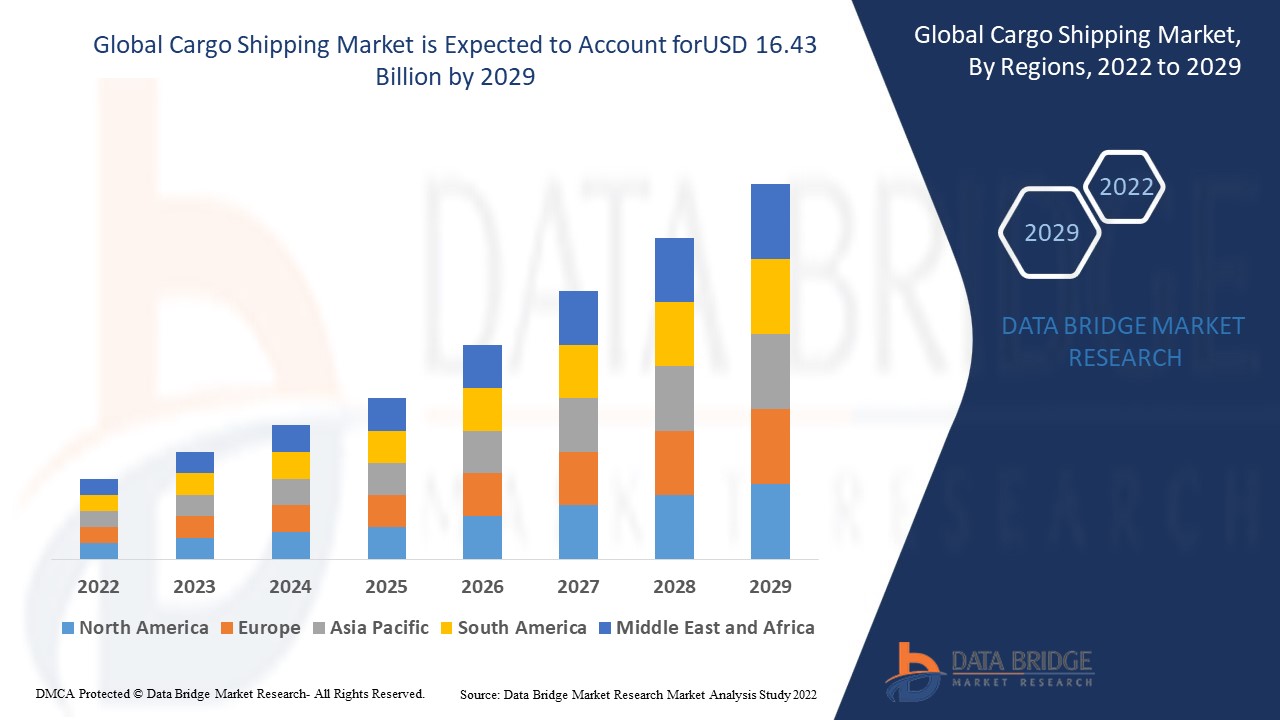
In 2024, the cargo shipping market was valued at over USD 2.5 trillion, and it is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.3% during the forecast period 2025 to 2030. Much of this growth is attributed to increased globalization, expanding manufacturing sectors, and the rising demand for energy and raw materials in emerging economies.
Key Market Drivers
-
Globalization and Trade Expansion
As international trade volumes grow, particularly between Asia-Pacific and North America, the demand for cargo shipping services increases. Free trade agreements and regional economic integrations have further encouraged cross-border trade. -
E-Commerce Growth
The explosive growth of e-commerce has accelerated the need for faster and more efficient shipping solutions. While air freight handles much of the expedited delivery, cargo ships still handle the majority of international bulk transport. -
Industrialization in Emerging Markets
Rapid industrial growth in developing countries such as India, China, Vietnam, and several African nations fuels the need for imports of raw materials and exports of finished goods—both of which drive cargo shipping demand. -
Technological Advancements
Innovations such as digital tracking, autonomous ships, blockchain in logistics, and improved port infrastructure are enhancing efficiency and reducing operational costs across the cargo shipping value chain. -
Sustainability Regulations
Stricter environmental regulations and the push for green shipping have prompted companies to invest in low-emission ships and alternative fuels, thereby modernizing the industry.
Market Challenges
Despite the promising outlook, the cargo shipping market faces several challenges:
-
Port Congestion and Delays
Major ports often face bottlenecks due to increasing container volumes and insufficient port infrastructure, leading to delays and higher costs. -
Geopolitical Uncertainty
Trade wars, maritime territorial disputes, and sanctions can disrupt global shipping routes and reduce demand in certain regions. -
Environmental Compliance Costs
Adapting to new IMO (International Maritime Organization) regulations regarding sulfur emissions and carbon footprints involves significant capital investment, affecting profitability. -
Crew Shortages and Labor Strikes
A lack of trained maritime personnel and frequent labor strikes in port cities can hinder operations and disrupt supply chains.
Market Segmentation
-
By Cargo Type
-
Container Cargo
Includes consumer goods, electronics, clothing, etc. Container shipping is expected to maintain dominance due to its flexibility and efficiency. -
Bulk Cargo
Includes coal, iron ore, grains, etc. Bulk shipping is crucial for heavy industries and energy production. -
Liquid Cargo
Comprises oil, gas, and chemicals. With global energy demands growing, this segment is poised for stable growth. -
General Cargo and Ro-Ro
Includes vehicles and machinery transported via specialized vessels.
-
-
By Vessel Type
-
Container Ships
-
Bulk Carriers
-
Tankers
-
Ro-Ro Ships
-
Multi-purpose Vessels
-
-
By End-User Industry
-
Manufacturing
-
Retail and E-commerce
-
Oil & Gas
-
Food & Agriculture
-
Automotive
-
Regional Insights
-
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific dominates the global cargo shipping market due to the presence of major exporters like China, Japan, and South Korea. Key ports such as Shanghai, Singapore, and Busan serve as global shipping hubs. -
North America
The United States, with its vast import-export requirements and advanced port facilities, contributes significantly to the cargo shipping market. The rise of e-commerce further bolsters demand. -
Europe
Europe has a mature market with strong infrastructure. However, environmental regulations are stricter, pushing companies to adopt green technologies. -
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East, particularly the UAE and Saudi Arabia, acts as a transshipment hub due to its strategic geographic location. Africa is emerging as a key market owing to its resource exports. -
Latin America
Brazil, Argentina, and Chile are prominent players due to their exports of agricultural products and minerals.
Key Players in the Market
Several major players dominate the cargo shipping industry through global fleets, advanced logistics capabilities, and integrated services. These include:
-
A.P. Moller-Maersk Group
-
Mediterranean Shipping Company (MSC)
-
CMA CGM Group
-
COSCO Shipping
-
Hapag-Lloyd
-
Evergreen Marine Corp.
-
ONE (Ocean Network Express)
These companies are investing heavily in digital transformation, fleet modernization, and green technologies to stay competitive.
Future Outlook
The cargo shipping market is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by increasing global trade, improved infrastructure, and technological advancements. Key trends shaping the future include:
-
Smart Ports and AI Integration
Ports are investing in automation, IoT, and AI-driven logistics to reduce turnaround times and enhance operational efficiency. -
Green Shipping Initiatives
Decarbonization efforts, including LNG-powered ships, hydrogen fuel, and carbon offsetting, will become standard industry practices. -
Autonomous Shipping
With pilot projects already underway, autonomous cargo ships may become operational in the next decade, reducing human error and costs. -
Blockchain and Digital Documentation
These technologies will streamline customs, reduce fraud, and ensure secure documentation across borders.
Get More Details:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-cargo-shipping-market
Conclusion
The cargo shipping market remains a linchpin of global commerce, enabling the smooth flow of goods across continents. Despite facing challenges such as environmental regulations and geopolitical risks, the market’s resilience and adaptability signal a strong growth trajectory in the coming years. With technological innovations and a push toward sustainability, the cargo shipping industry is poised to redefine itself in a rapidly globalizing and digitizing world.