Best Treatments for Chronic Lower Back Pain | Expert Tips
Chronic Lower Back Pain | Expert Tips

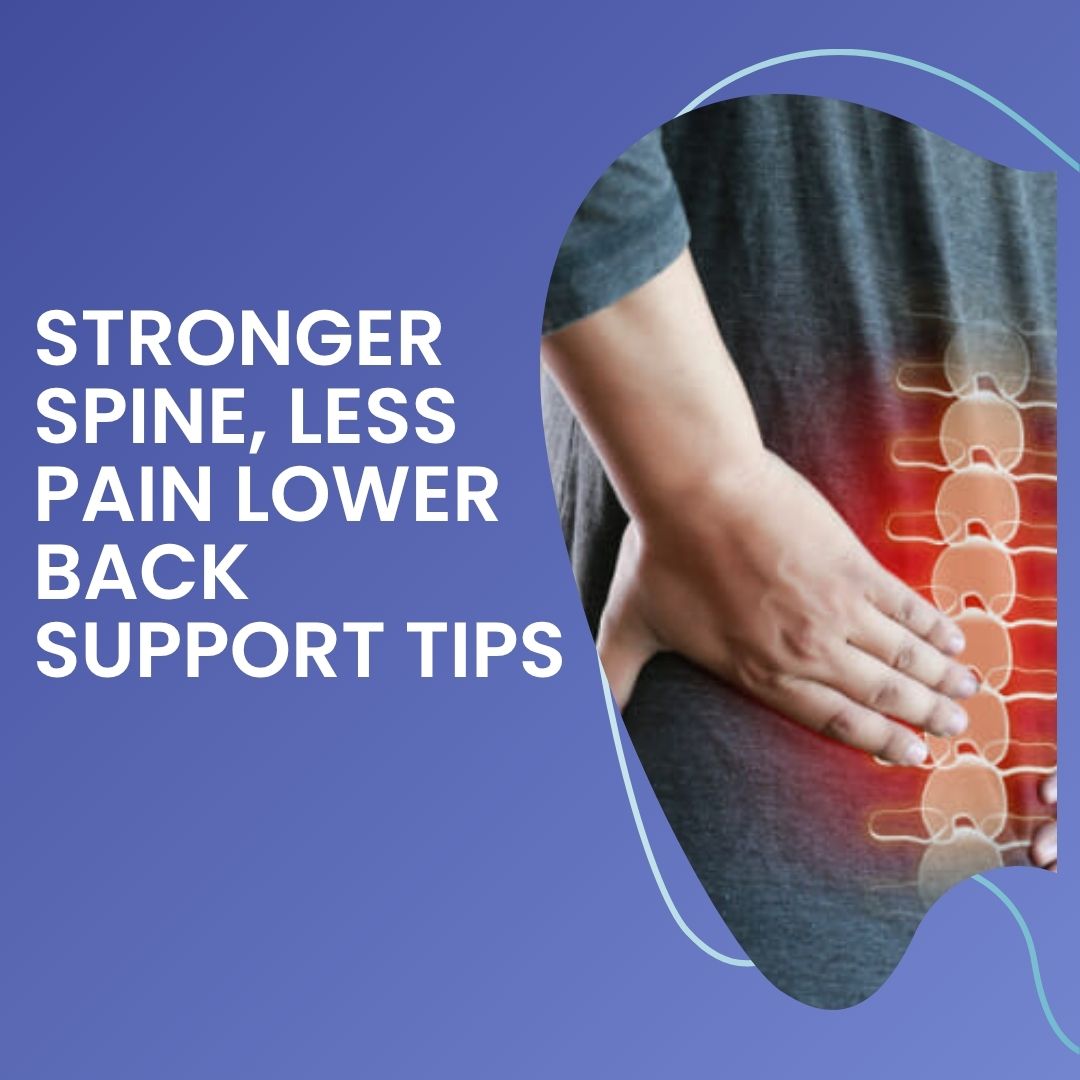
Chronic lower back pain is one of the most common and long-standing medical conditions that touch millions of lives worldwide. It is defined as more than 12 weeks of pain, even though the original insult or source of pain may have resolved. The condition has been shown to interfere with daily functions, work capacity, sleep, and overall quality of life. A number of treatment options have been proposed to decrease symptomatology and promote mobility.
In cases of intractable chronic pain or pain that is not manageable with conventional treatments, medications like Aspadol 100mg have been used by healthcare providers. The medication contains Tapentadol as its active ingredient. It belongs to the opioid analgesic category and works by altering the way the brain as well as the nervous system respond to pain. Tapentadol has been used to treat moderate to severe pain in patients who have proven to be resistant to other medications. It is administered under strict medical supervision due to its side effects and dependency potential.
Causes of Chronic Lower Back Pain
Chronic lower back pain can be caused by a number of factors. It is most often associated with:
-
Degenerative disc disease
-
Spinal stenosis
-
Herniated or bulging discs
-
Arthritis of the spine
-
Injuries or trauma
-
Poor posture or a sedentary lifestyle
The cause of chronic pain is not always identified. Pain in such cases will frequently persist even when the initial injury has healed. A complete examination by a health care provider is typically warranted in order to properly diagnose and plan treatment.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
The majority of chronic lower back pain patients have been treated successfully with non-surgical treatment. They are:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy programs have been considered the first line of treatment. Excesses have been tailored to individual needs to build abdominal and back muscles. Stretching, aerobic conditioning, and posture training have also been added to enhance mobility and reduce pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Alternating heat and cold packs have been utilized to reduce pain and inflammation. Cold packs decrease swelling, whereas heat has been used to induce muscle relaxation and improve blood supply to the affected area.
Lifestyle Modifications
Weight reduction, ergonomic adjustments, and smoking cessation have been recommended to improve spinal health. Obesity and poor posture have been recognized as common causative agents of chronic back pain.
Over-the-Counter Pain Medications
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, have been used in treating mild to moderate back pain. They reduce inflammation and provide short-term relief.
Prescription Drug for Chronic Pain
If over-the-counter medicines prove to be inadequate in relief, then prescription drugs are normally pursued. These are:
Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants have been administered to relax spasms and tension within the muscles that may be contributing to back pain. They are only for short-term relief.
Opioids
For more severe chronic back pain, opioids like **Tapentadol**, which is available as **Aspadol 100mg**, can be employed. It works by binding to opioid receptors and inhibiting norepinephrine reuptake, producing dual-action pain inhibition. It is normally reserved for patients who have not responded to other analgesics. Long-term administration is closely monitored due to the potential for tolerance, dependency, and side effects such as dizziness, constipation, and somnolence.
Minimally Invasive Procedures
Non-pharmacologic interventions failing to provide adequate relief may have minimally invasive procedures recommended. These include:
Epidural Steroid Injections
Steroids have been injected in the epidural space surrounding the spinal cord in an effort to reduce inflammation and pain relief. It is a short-term solution to relief that is most commonly administered as part of a comprehensive treatment regimen.
Nerve Blocks
Injections into specific nerves have been used to block pain signals. These have been performed under imaging guidance and are often used both for diagnosis and for treatment.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is reserved for last resort and is only usually provided after failure of conservative treatments. The following surgical procedures are typical:
Spinal Fusion
Two or more vertebrae are joined permanently to eliminate motion between them. The operation stabilizes the spine and does away with pain due to movement.
Discectomy
The portion of a herniated disc pressing on a nerve root is removed to eliminate pain. It is normally used in cases of sciatic nerve pain.
Laminectomy
Partial removal of part of the vertebra (lamina) has been performed to decrease pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
Complementary Therapies
Chronic lower back pain has also been treated with treatments other than standard treatment. Such treatment is designed to supplement standard treatment and improve quality of life.
Acupuncture
Thin needles have been inserted into specific points on the body to stimulate nerves and muscles. Acupuncture has been found to reduce pain and improve function in selected patients.
Chiropractic Care
Manipulation of the spine by hand has been provided by chiropractors to restore alignment and mobility. The treatment is most often administered to patients with musculoskeletal disorders.
Massage Therapy
Therapeutic massage has been used to relieve muscle tension and encourage circulatory blood flow. Weekly sessions have the possibility of decreasing degrees of chronic pain.
Psychological Support
Chronic pain affects the mental state. Symptoms such as depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances are likely to develop because of persistent discomfort.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT has also been offered to assist patients in dealing with pain through behavioral and psychological strategies. It seeks to change maladaptive thinking patterns and improve coping strategies.
Support Groups and Counseling
Talking to others with the same problems or undergoing professional mental health treatment has been shown to improve emotional functioning and compliance with medication.
Conclusion
Chronic lower back pain has a significant impact on quality of life. But effective treatment measures have been offered with the combination of physical therapy, medication, minimally invasive procedures, and mental guidance. The medication, such as Aspadol 100mg, having Tapentadol as the active constituent, has also been utilized in certain cases to treat severe pain under the supervision of a doctor. The right treatment process has been tailored based on etiology, intensity of symptoms, and requirements of the patient. Medical consultation remains a priority for effective diagnosis and treatment of chronic lower back pain.