AI and Predictive Analytics in Natural Disaster Management
Introduction
Natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, wildfires, and floods are increasingly frequent and severe due to climate change and urban expansion. These catastrophic events not only cause loss of life and property but also disrupt economies and strain emergency services. Predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionizing how we anticipate, respond to, and recover from natural disasters in this dynamic environment.
Definition
Natural Disaster Management refers to the organized efforts and strategies implemented to prepare for, respond to, and recover from natural calamities such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires. It involves risk assessment, planning, resource allocation, emergency response, and rehabilitation to minimize the impact of disasters on lives, property, and the environment.
Understanding AI and Predictive Analytics
Artificial Intelligence refers to computer systems that mimic human intelligence, including capabilities like learning, reasoning, and self-correction. Utilizing data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques, predictive analytics determines the probability of future events based on past data. When combined, these technologies enable the development of intelligent systems that can forecast natural disasters, assess risk levels, and recommend actions in real-time.
Enhancing Early Warning Systems
The enhancement of early warning systems is one of the most important uses of AI in disaster management. Traditional systems often rely on limited data and predefined rules, which can lead to delayed or inaccurate alerts.
AI-Powered Earthquake Detection:
AI models trained on seismic data can detect the smallest tremors and distinguish between different types of seismic waves. For example, Google has deployed AI models in Android smartphones that transform them into mini-seismographs, enabling real-time earthquake detection and alerts in regions without traditional sensors.
Flood Forecasting:
Predictive analytics models integrate satellite data, rainfall measurements, topography, and historical flood patterns to forecast flood events. These models can issue warnings days in advance, allowing residents and emergency responders to prepare effectively.
Hurricane and Cyclone Tracking:
AI systems can analyze satellite imagery, ocean temperatures, and wind patterns to predict the formation and path of hurricanes. This enables more accurate evacuation planning and resource deployment, potentially saving thousands of lives.
Real-Time Disaster Monitoring and Response
Beyond prediction, AI plays a pivotal role during the disaster response phase. Real-time monitoring, decision-making, and logistics management are critical when every second counts.
Drones and Computer Vision:
AI-equipped drones can survey disaster zones, assess structural damage, locate survivors, and provide high-resolution imagery to first responders. Computer vision algorithms analyze this data instantly, offering insights far faster than human teams could achieve.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants:
During disasters, public communication is essential. AI-powered chatbots provide up-to-date information on evacuation routes, shelter availability, and safety procedures through websites and social media, reducing panic and misinformation.
Resource Allocation and Logistics:
Machine learning algorithms optimize the allocation of emergency supplies, medical assistance, and rescue teams based on real-time data. These systems consider road conditions, weather forecasts, and population density to streamline aid delivery.
Post-Disaster Recovery and Risk Assessment
The role of AI extends beyond immediate disaster response to long-term recovery and risk reduction.
Damage Assessment:
AI can assess post-disaster damage using satellite images and aerial surveys. Machine learning models classify areas based on damage severity, helping governments prioritize rebuilding efforts and allocate resources efficiently.
Insurance and Financial Modeling:
Predictive analytics supports insurance companies in evaluating risks, determining premiums, and managing claims. AI models analyze past disaster data and property conditions to forecast potential losses and speed up claims processing for affected individuals.
Urban Planning and Resilience Building:
City planners and policymakers use AI to simulate various disaster scenarios and evaluate the effectiveness of infrastructure investments. For example, predictive models can highlight flood-prone areas, enabling the construction of better drainage systems or relocation of vulnerable communities.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
IBM’s Watson and Disaster Relief:
IBM’s Watson has been employed in several disaster relief initiatives. During the 2010 Haiti earthquake, AI helped translate Creole texts to aid international rescue teams. In recent years, Watson’s cognitive capabilities have been used to optimize logistics in disaster zones.
One Concern:
One Concern is a startup that uses AI and predictive analytics to model the impact of earthquakes, floods, and other disasters. Their platform helps cities and governments simulate scenarios and plan interventions with a focus on community resilience.
NASA and Machine Learning for Wildfires:
NASA uses machine learning algorithms to predict wildfire risks and monitor fire progression using satellite imagery and environmental data. This real-time insight enables early evacuations and strategic firefighting efforts.
Challenges in Implementing AI for Disaster Management
Despite its promise, integrating AI into disaster management is not without challenges:
- Data Availability and Quality: AI systems require large volumes of high-quality, real-time data, which may not be readily available in developing regions.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Many disaster-prone areas lack the digital infrastructure necessary for deploying AI-based systems.
- Algorithm Bias: Predictive models may reflect biases in the data, leading to uneven resource distribution or inaccurate predictions.
- Privacy and Ethics: The use of personal and geolocation data during disasters raises concerns around privacy and ethical use.
Addressing these challenges requires international cooperation, public-private partnerships, and clear regulatory frameworks to ensure that AI serves all communities equitably.
The Future of AI in Disaster Management
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in natural disaster management will become increasingly significant. Some emerging trends include:
- Edge Computing: AI models run directly on local devices, reducing latency and enabling faster decision-making in remote or offline areas.
- Integration with IoT: Smart sensors, wearable devices, and connected infrastructure can feed real-time data to AI systems for continuous monitoring.
- AI for Climate Change Adaptation: Beyond immediate disaster response, AI is being used to model long-term climate risks and guide sustainable development practices.
Governments, humanitarian organizations, and tech companies are investing heavily in AI-driven disaster resilience. As these systems become more robust and accessible, we can expect a future where early warnings are more accurate, emergency responses more efficient, and recovery efforts more effective.
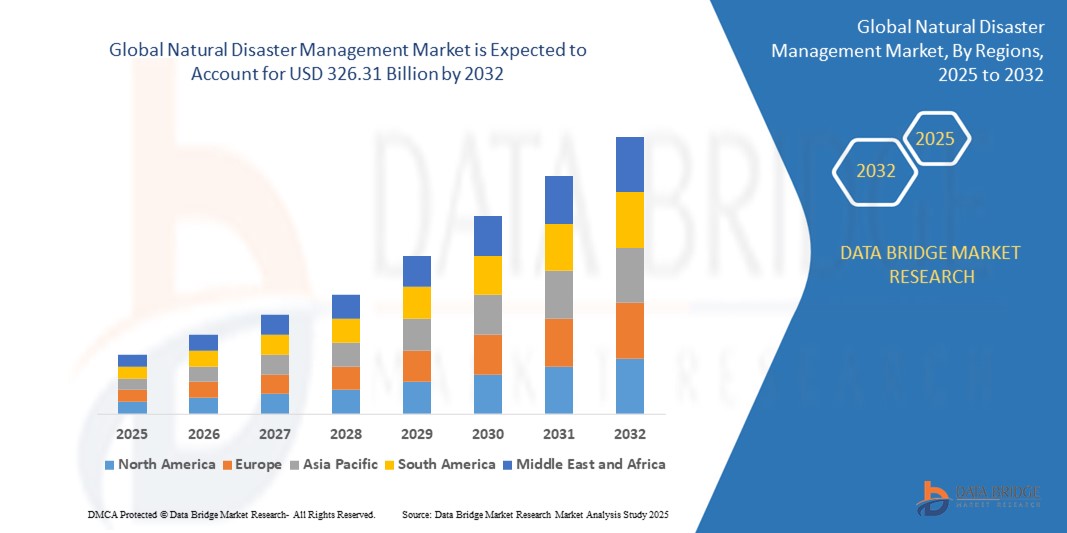
Growth Rate of Natural Disaster Management Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the size of the global natural disaster management market was estimated at USD 137.58 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.40% to reach USD 326.31 billion by 2032.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-natural-disaster-management-market
Conclusion
AI and predictive analytics are revolutionizing the field of natural disaster management. From forecasting and early warning to real-time response and recovery, these technologies offer powerful tools to reduce the impact of natural disasters and save lives. While challenges remain, continued innovation and collaboration hold the key to building smarter, more resilient communities prepared to face the uncertainties of a changing world.




