Complete Guide to Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0 with Best Examples

Introduction
The internet has gone through a fascinating evolution since it was first introduced to the world. From simple static websites with text and images to today’s immersive digital experiences with blockchain, artificial intelligence, and the metaverse, each phase has transformed the way we connect, share, and do business. These stages are often referred to as Web 1.0, Web 2.0, Web 3.0.
Understanding the differences between these versions is essential for anyone who wants to grasp how the internet has evolved and where it is heading. In this complete guide, we will explore Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0. with examples, explain how they work, highlight their benefits and drawbacks, and discuss which stage offers the greatest opportunities for the future.
What is Web 1.0 ? – The Beginning of the Internet
Web 1.0 refers to the earliest version of the World Wide Web, developed between 1989 and the early 2000s. Often called the “read-only web”, it mainly consisted of static HTML pages. Websites were like digital brochures: they displayed information but offered little to no interaction.
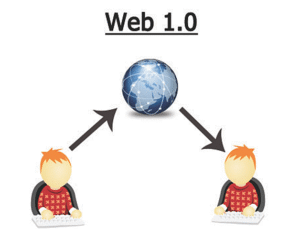
How Web 1.0 Worked
- Information was stored on servers and presented in a static format.
- Users could only read content, without commenting, sharing, or uploading.
- Navigation was limited to hyperlinks.
Features of Web 1.0
- Static pages with simple designs.
- Limited multimedia (basic text and images).
- No interactivity between site owners and visitors.
- Centralized control of content by site creators.
Examples of Web 1.0
- Yahoo! Directory (early version) – simple lists of links to websites.
- GeoCities – a platform for personal static homepages.
- Ask Jeeves (early search engine) – text-based search with minimal functionality.
- MSN Web Portal (late 1990s) – news and static content.
Benefits of Web 1.0
- Simple and easy to build.
- Reliable and stable since nothing was dynamic.
- Good for basic information sharing.
Drawbacks of Web 1.0
- No real-time updates.
- No user participation or content creation.
- Poor user experience compared to today.
What is Web 2.0? – The Social and Interactive Web
Web 2.0 represents the second generation of the internet, starting around 2004 and continuing today. It shifted the web from static to dynamic. Users could now interact with content, upload their own, and build communities. This phase is also called the “read-write web.”
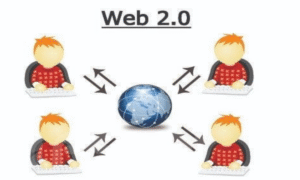
How Web 2.0 Works
- Built on dynamic web technologies like JavaScript, CSS, AJAX.
- Data is stored in centralized databases controlled by companies.
- Users can create accounts, upload content, and interact with others.
Features of Web 2.0
- Social media platforms for interaction and sharing.
- User-generated content (blogs, videos, images, reviews).
- Mobile-first applications and cloud computing.
- E-commerce and online payments.
Examples of Web 2.0
- Facebook, Twitter (X), Instagram – social networks for global interaction.
- YouTube – community-driven video platform.
- Wikipedia – collaboratively created knowledge base.
- Google Docs – real-time document collaboration.
- Amazon, eBay – online marketplaces connecting buyers and sellers.
Benefits of Web 2.0
- Encourages user participation and creativity.
- Easy communication and collaboration across the globe.
- Massive growth of online businesses and e-commerce.
- Access to free tools, social networking, and cloud services.
Drawbacks of Web 2.0
- Centralized control – companies own and control data.
- Privacy issues – user information often exploited for ads.
- Risk of censorship and manipulation.
- High dependence on tech giants.
What is Web 3.0? – The Decentralized and Intelligent Web
Web 3.0 is the next step in internet evolution, still emerging today. It is often called the “read-write-own web” because it is based on decentralization, blockchain, and artificial intelligence. Unlike Web 2.0, where tech companies control data, Web 3.0 allows users to own and control their data.

How Web 3.0 Works
- Built on blockchain technology and smart contracts.
- Uses decentralized storage instead of centralized databases.
- Employs AI, machine learning, and semantic web principles.
- Enables token-based economies with cryptocurrencies and NFTs.
Features of Web 3.0
- Decentralization – no single company controls the data.
- Smart contracts – automated, transparent transactions.
- Interoperability – apps can connect across blockchains.
- Metaverse – virtual environments with real-world economies.
- AI integration – intelligent search, personalization, automation.
Examples of Web 3.0
- Ethereum – blockchain for smart contracts and DApps.
- Uniswap & Aave – decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms.
- IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) – decentralized file storage.
- Decentraland & Sandbox – blockchain-powered virtual worlds.
- Brave Browser – privacy-focused browser with built-in crypto rewards.
Benefits of Web 3.0
- User data ownership and privacy protection.
- Reduced risk of censorship or single-point failure.
- Transparent and secure transactions.
- New opportunities through decentralized finance, NFTs, and metaverse.
Drawbacks of Web 3.0
- Still in development and adoption is limited.
- Scalability and usability issues.
- Complex for beginners.
- Regulatory uncertainty around blockchain and crypto.
Comparison of Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0
| Feature | Web 1.0 | Web 2.0 | Web 3.0 |
| Nature | Read-only | Read & Write | Read, Write & Own |
| Control | Centralized | Centralized (big tech) | Decentralized |
| Content | Static pages | Dynamic, user-generated | Decentralized, intelligent |
| Examples | Yahoo! Directory, GeoCities | Facebook, YouTube, Wikipedia | Ethereum, Decentraland, Uniswap |
| User Role | Consumer | Creator & consumer | Owner & participant |
| Technology | HTML | JavaScript, CSS, AJAX | Blockchain, AI, Smart contracts |
Which One is the Best? Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0
- Web 1.0 laid the foundation of the internet.
- Web 2.0 transformed the web into a social and interactive space.
- Web 3.0 holds the future by giving ownership, transparency, and decentralization.
While Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 were critical in shaping today’s internet, the best for the future is Web 3.0, as it empowers users with control over their data and provides innovative financial and social opportunities.
Conclusion
The internet has evolved from Web 1.0 Web 2.0 Web 3.0 each stage offering unique features and opportunities. Web 1.0 was static and read-only, Web 2.0 is dynamic and social, and Web 3.0 is decentralized and intelligent.
By understanding their differences and examples, we can see how the web has moved from simple information sharing to interactive communities and now towards decentralized ownership. The future of the internet is likely to be shaped by Web 3.0, with blockchain, AI, and the metaverse leading the way.




